Part 2: How CI/CD methodologies can be applied to 5G RAN Testing and Deployment
How CI/CD methodologies can be applied to 5G RAN Testing and Deployment
The following is Part 2 of our multi-part Blog Series, "Replicate your 5G Open RAN network and enable zero-touch test orchestration". Part 1 was published here: Part 1: How 5G/O-RAN and cloud native architectures introduce new complexities for testing labs
With the advent of software-centric applications, CI/CD methodologies and continuous testing workflows were introduced to improve end-user applications and experiences. Could these same principles and methods be used to test things that are not virtual - like parts of 5G RAN?
The 5G core and upper layers of the RAN are moving to software workloads, which allows the services to be served from different physical locations. CI/CD applies well in these cases but what about the physical attributes of the wireless network like RRUs and the mobile devices at the other end? The mobile network also includes the physical medium of RF where different engineering techniques such as MIMO and carrier aggregation can be used to increase coverage and bandwidth. These are essential to delivering a service to the paying customer. How do we bring these parts of the system into the cycle of rapid testing?
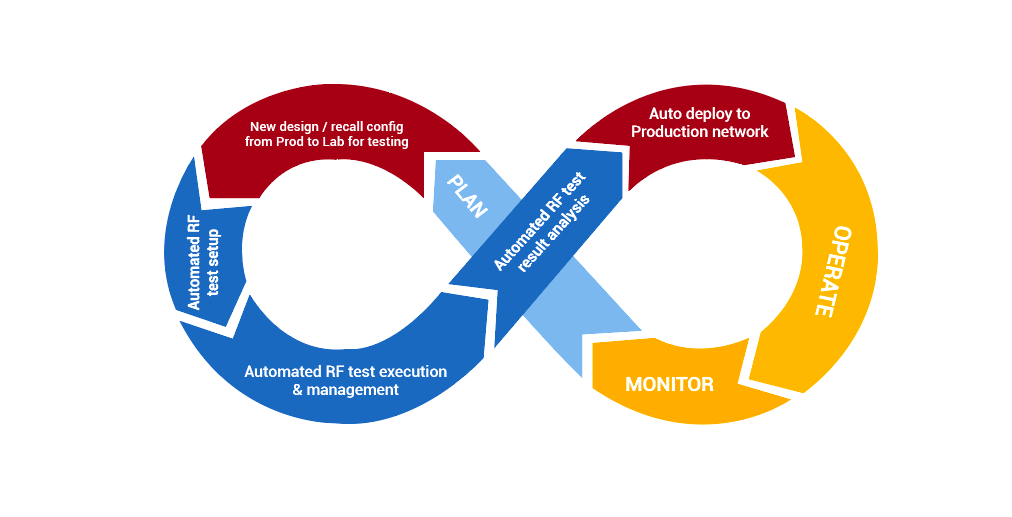
This adaptation of the CI/CD diagram shows how we can start to think about it. There are parallel activities in the physical testing world that match those in the software world. The light blue region shows the physical equivalent of software development activities, and the dark blue region shows the physical testing activities. The CI/CD model fits – but we’re not there yet. To be truly CI/CD everything here must be automated. This is straightforward when dealing with virtual or cloud-based portions of the network, but the physical elements shown in the dark blue regions are a different matter.
This part of the CI/CD loop needs new automation tools that can orchestrate all the physical elements in the lab together to automate the test setup, execution, and analysis of the results. By using a mirror lab replica of the mobile production network, it may be possible to introduce test orchestration automation to help employ CI/CD practices in the wireless test lab.
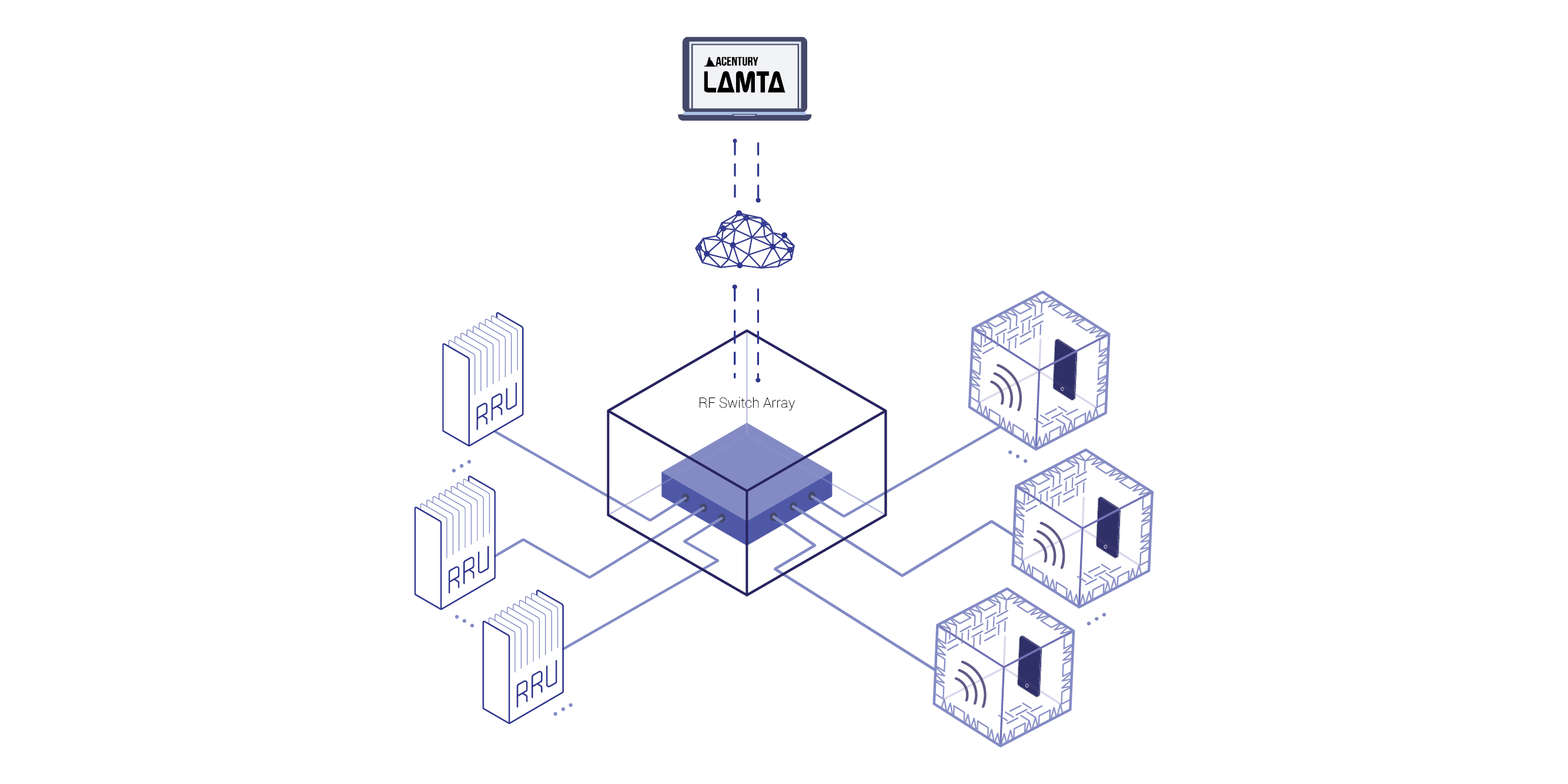
A mirror lab replica of a production network that uses an orchestration layer can help lab testers implement faster and more sophisticated testing workflows which will optimize operational efficiency.
Is this the same as testing automation that operators have already paid for?
Test automation is a term frequently used to describe the automation activities of the test themselves; however, to fully embrace CI/CD methodologies the process must also include all the activities surrounding the execution of rapid and frequent test cycles. Activities such as test planning, equipment setup and equipment configuration are time-consuming and manual. Other activities that can impact lab operational efficiency: scheduling and managing people and lab equipment resources; orchestrating all the network elements and radio network equipment; collecting, organizing, and interpreting test results.
A well-designed mirror lab can address these pain points. Using an orchestration layer can help manage and control test set up and configuration, people and equipment resource scheduling, and results analysis and evaluation.
If you want to learn more about how Acentury’s LAMTA solution helped address these pain points with a Tier 1 mobile network operator, please refer to our customer case study: Customer Case Study
- To learn more about Acentury LAMTA's product features, refer to the product web page: HERE
- To learn about LAMTA's RF test position solution: HERE
Stay tuned for Part 3 in our Blog Series where we explore how a mirror lab replica of a production network can be design and architected to test 5G networks.
Have a question or comment?
We'd love to hear it. Fill out our General Inquiry Form or reach us directly at: info@acentury.co
CONTACT US